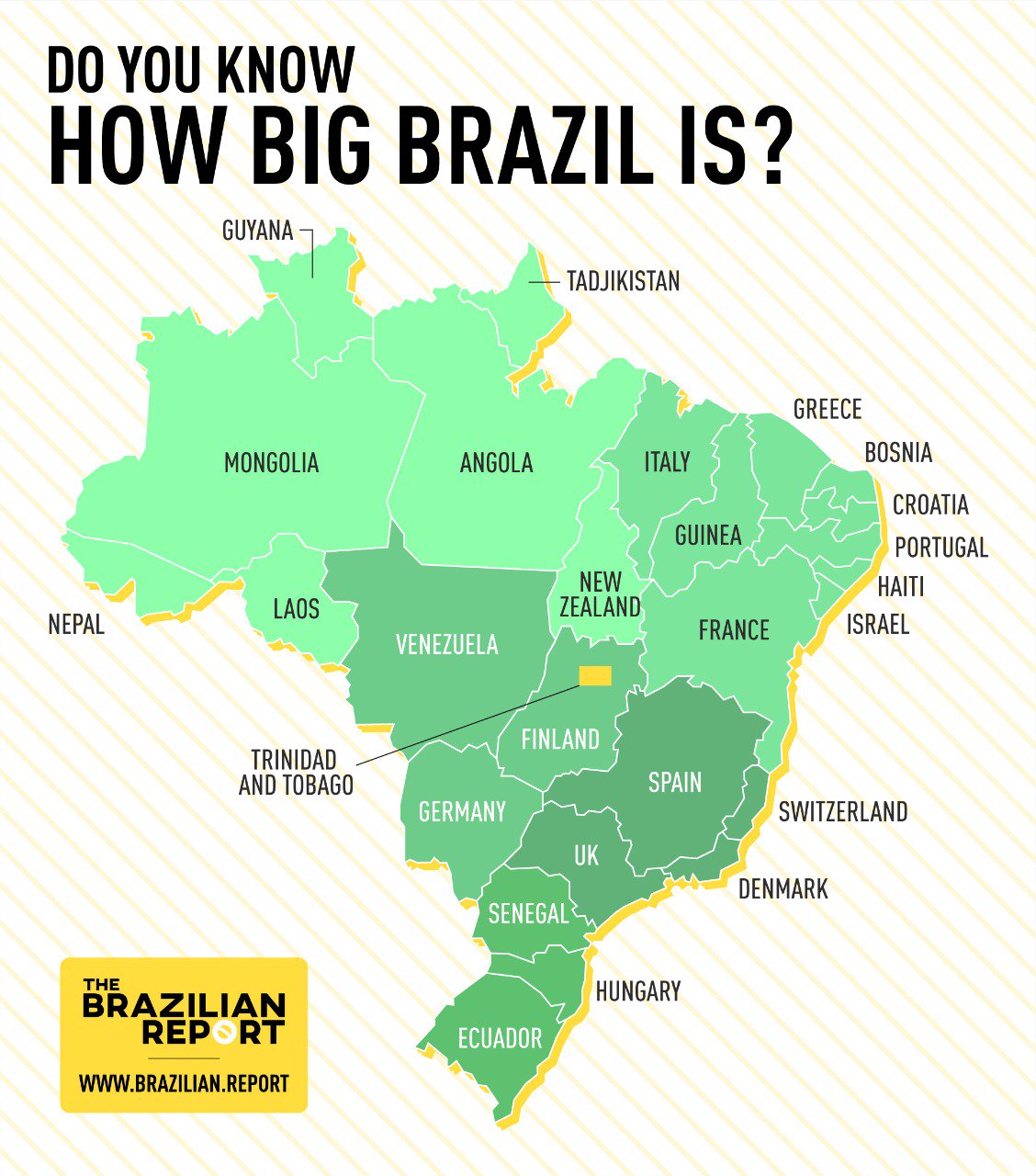
How big is Brazil? Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world, covering an area of 8.5 million square kilometers (3.3 million square miles).
Brazil's size gives it a diverse range of climates and ecosystems, from the Amazon rainforest to the Pantanal wetlands. The country is also home to a wide variety of plant and animal life, including many endangered species.
Brazil's size has also played a role in its history and development. The country's vast territory has made it difficult to govern and has led to regional disparities in economic development. However, Brazil's size has also given it a strategic advantage, as it controls access to the Amazon River and the Atlantic Ocean.
brazil country size
Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world, covering an area of 8.5 million square kilometers (3.3 million square miles). Its size has a profound impact on its geography, climate, economy, and culture.
- Geographical Diversity: Brazil's vast size encompasses a wide range of ecosystems, from the Amazon rainforest to the Pantanal wetlands.
- Climate Zones: The country's size contributes to its diverse climate zones, from the tropical north to the temperate south.
- Economic Powerhouse: Brazil's size and natural resources make it a major economic power, with a strong agricultural and industrial base.
- Cultural Tapestry: The country's size has fostered a rich cultural diversity, with influences from indigenous, European, and African traditions.
- Global Significance: Brazil's size and strategic location give it a significant role in international affairs, particularly in environmental and economic matters.
In conclusion, Brazil's vast size is a defining characteristic that shapes its geography, climate, economy, culture, and global influence. From the Amazon rainforest to the bustling cities of So Paulo and Rio de Janeiro, Brazil's size has played a crucial role in its development and continues to influence its present and future.
Geographical Diversity
The vast size of Brazil has resulted in a remarkable geographical diversity, showcasing a wide array of ecosystems within its borders.
- Amazon Rainforest:
Covering over 60% of Brazil's territory, the Amazon rainforest is the largest rainforest in the world and is home to an estimated 10% of the world's known species. Its immense size and biodiversity make it a crucial ecosystem for global climate regulation and biodiversity conservation.
- Pantanal Wetlands:
Located in western Brazil, the Pantanal is the world's largest tropical wetland, covering an area of over 150,000 square kilometers. This unique ecosystem is home to a diverse array of plant and animal life, including the endangered giant river otter and hyacinth macaw.
- Cerrado Savanna:
Covering over 2 million square kilometers, the Cerrado is a vast savanna ecosystem located in central Brazil. It is characterized by its unique vegetation, which includes both trees and grasses, and is home to a wide variety of wildlife, including the maned wolf and giant anteater.
- Atlantic Forest:
Stretching along the eastern coast of Brazil, the Atlantic Forest is a diverse rainforest ecosystem that is home to over 20,000 plant species and 1,300 animal species. It is one of the most biodiverse forests in the world and plays a crucial role in regulating the climate and providing water resources.
The geographical diversity of Brazil, resulting from its vast size, has a profound impact on the country's climate, economy, and culture. It contributes to Brazil's role as a global leader in biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
Climate Zones
Brazil's vast size plays a crucial role in shaping its diverse climate zones. The country's extensive latitudinal range, spanning from the equator to the subtropics, combined with its varied topography, creates a wide range of climatic conditions.
In the northern regions of Brazil, near the equator, the climate is predominantly tropical, characterized by high temperatures and abundant rainfall throughout the year. This region is home to the Amazon rainforest, which benefits from the consistent warmth and moisture.
Moving southward, the climate gradually transitions to subtropical in central Brazil. This region experiences distinct seasons, with hot, humid summers and mild, dry winters. The Cerrado savanna, located in central Brazil, is adapted to these seasonal changes.
In the southernmost regions of Brazil, the climate becomes temperate, with cooler temperatures and more evenly distributed rainfall. This region is home to the Atlantic Forest, which thrives in the moderate climate conditions.
The diverse climate zones of Brazil have a significant impact on the country's agriculture, ecosystems, and overall habitability. Understanding the connection between Brazil's size and its climate zones is crucial for effective land management, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable development.
Economic Powerhouse
Brazil's vast size and abundant natural resources have played a significant role in its economic development, making it a major economic power in the global market.
- Agricultural Powerhouse:
Brazil's extensive land area provides vast agricultural potential. The country is a leading producer of soybeans, coffee, sugarcane, and other agricultural commodities. Its size allows for large-scale farming operations, contributing significantly to Brazil's agricultural exports and economic growth.
- Mineral Wealth:
Brazil possesses a wealth of mineral resources, including iron ore, copper, gold, and diamonds. The country's size and geological diversity have resulted in significant mineral deposits, which have fueled its mining industry and contributed to its economic development.
- Industrial Base:
Brazil's size has enabled the development of a diverse industrial base. The country has invested in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace. Its large domestic market and access to raw materials have supported industrial growth and economic diversification.
- Global Trade:
Brazil's size and strategic location have facilitated its participation in global trade. The country has a strong export-oriented economy, with its agricultural and industrial products reaching markets worldwide. Its size allows for efficient transportation and logistics, enhancing its global trade competitiveness.
In conclusion, Brazil's size and natural resources have been instrumental in its economic development and status as a major economic power. The country's vast agricultural lands, mineral wealth, industrial base, and global trade connections are all factors that contribute to its economic strength and influence in the global economy.
Cultural Tapestry
Brazil's vast size has played a pivotal role in fostering a rich and diverse cultural tapestry. The country's extensive territory has allowed for the preservation and interaction of distinct cultural traditions, resulting in a unique blend of indigenous, European, and African influences.
The indigenous peoples of Brazil, with their diverse languages, customs, and spiritual beliefs, have significantly contributed to the country's cultural heritage. Their traditions continue to influence art, music, and literature, particularly in rural and indigenous communities.
The arrival of European colonizers, primarily from Portugal, brought new cultural elements that fused with existing indigenous traditions. This interaction gave rise to new cultural expressions, such as the Afro-Brazilian religion of Candombl, which combines African and Catholic beliefs.
Later, Brazil received a significant influx of immigrants from various European countries, including Italy, Germany, and Spain. These immigrants brought their own cultural traditions, which further enriched Brazil's cultural landscape. The result is a vibrant mix of languages, music, cuisine, and festivals that reflect Brazil's diverse heritage.
Understanding the connection between Brazil's size and its cultural diversity is crucial for appreciating the country's unique identity. The vast territory has allowed for the preservation and interaction of distinct cultural traditions, creating a rich and dynamic cultural tapestry that is celebrated throughout Brazil and beyond.
Global Significance
Brazil's vast size and strategic location have profound implications for its global significance, particularly in environmental and economic matters.
- Environmental Stewardship:
As home to the Amazon rainforest, the world's largest rainforest, Brazil plays a critical role in global climate regulation and biodiversity conservation. Its size and geographical diversity make it a key player in international environmental agreements and negotiations.
- Economic Powerhouse:
Brazil's size and natural resources have contributed to its economic strength. As a major exporter of agricultural commodities and minerals, Brazil has a significant influence on global markets and economic policies.
- Regional Leadership:
Brazil's size and strategic location make it a natural leader in South America. It plays a key role in regional organizations and initiatives, promoting economic integration, political stability, and sustainable development.
- Global Partnerships:
Brazil's size and global significance have led to the formation of strategic partnerships with countries and organizations around the world. These partnerships focus on areas such as trade, technology, and environmental cooperation.
In conclusion, Brazil's vast size and strategic location have a profound impact on its global significance. From environmental stewardship to economic power and regional leadership, Brazil's size empowers it to play a pivotal role in international affairs and shape the global agenda.
Frequently Asked Questions about "brazil country size"
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding Brazil's vast size and its implications.
Question 1: How does Brazil's size compare to other countries?
Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world, with a total area of approximately 8.5 million square kilometers (3.3 million square miles). It is larger than the entire continent of Europe and nearly half the size of the United States.
Question 2: What are the key implications of Brazil's size?
Brazil's size has a profound impact on its geography, climate, economy, culture, and global significance. It contributes to the country's diverse ecosystems, abundant natural resources, economic power, cultural tapestry, and its role in environmental stewardship and international affairs.
Summary: Understanding the implications of Brazil's size is crucial for comprehending its unique identity, economic strength, and global influence. Brazil's vast territory shapes its geography, climate, culture, and economy, making it a significant player on the world stage.
Conclusion
In exploring the multifaceted implications of "brazil country size," we have uncovered its profound impact on the nation's geography, climate, economy, culture, and global significance. Brazil's vast territory, spanning over 8.5 million square kilometers, has shaped its diverse ecosystems, from the Amazon rainforest to the Pantanal wetlands. This size has also contributed to Brazil's economic power, making it a major player in agriculture, mining, and industry, with a strong global trade presence.
Furthermore, Brazil's size has fostered a rich cultural tapestry, blending indigenous, European, and African influences, resulting in a vibrant and diverse cultural landscape. Its global significance extends to environmental stewardship, as Brazil plays a critical role in preserving the Amazon rainforest and mitigating climate change. The country's size and strategic location also make it a regional leader and a key player in international affairs.
In conclusion, Brazil's vast size is not merely a geographical attribute but a defining characteristic that has shaped its identity, economy, culture, and global influence. Understanding the implications of Brazil's size is crucial for comprehending the complexities of this nation and its role in the world.